Could a DIY ultrasound be in your future? UBC breakthrough opens door to $100 ultrasound machine
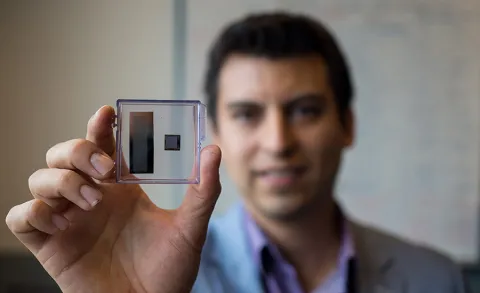
Engineers at the University of British Columbia have developed a new ultrasound transducer, or probe, that could dramatically lower the cost of ultrasound scanners to as little as $100. Their patent-pending innovation—no bigger than a Band-Aid—is portable, wearable and can be powered by a smartphone.
Conventional ultrasound scanners use piezoelectric crystals to create images of the inside of the body and send them to a computer to create sonograms. Researchers replaced the piezoelectric crystals with tiny vibrating drums made of polymer resin, called polyCMUTs (polymer capacitive micro-machined ultrasound transducers), which are cheaper to manufacture.
“Transducer drums have typically been made out of rigid silicon materials that require costly, environment-controlled manufacturing processes, and this has hampered their use in ultrasound,” said study lead author Carlos Gerardo, a PhD candidate in electrical and computer engineering at UBC. “By using polymer resin, we were able to produce polyCMUTs in fewer fabrication steps, using a minimum amount of equipment, resulting in significant cost savings.”
Sonograms produced by the UBC device were as sharp as or even more detailed than traditional sonograms produced by piezoelectric transducers, said co-author Edmond Cretu, professor of electrical and computer engineering.
“Since our transducer needs just 10 volts to operate, it can be powered by a smartphone, making it suitable for use in remote or low-power locations,” he added. “And unlike rigid ultrasound probes, our transducer has the potential to be built into a flexible material that can be wrapped around the body for easier scanning and more detailed views–without dramatically increasing costs.”

Left to right: Edmond Cretu, Carlos D. Gerardo and Robert Rohling. Credit: Clare Kiernan
Co-author Robert Rohling, also a professor of electrical and computer engineering, said the next step in the research is to develop a wide range of prototypes and eventually test their device in clinical applications.
“You could miniaturize these transducers and use them to look inside your arteries and veins. You could stick them on your chest and do live continuous monitoring of your heart in your daily life. It opens up so many different possibilities,” said Rohling.
The research was published recently in Nature Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
Contact lou.bosshart@ubc.ca to obtain a copy or to schedule interviews with the researchers.
Find other stories about: Carlos Gerardo, Edmond Cretu, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ultrasound